Research and Development of CAPP Template Customization System (4)
3.3 Template Sub-Element Object Attribute Definition
After the drawing is finished, the system temporarily saves the graphic on the screen to the linked list, and the coordinates of the graphic are stored in it. At this point, the graphic element is not added to the card template, and its properties must be defined before the graphic element can be saved. When defining graphic element properties, the system provides a picking function for graphic elements. Once a graphic element is selected, it can be assigned the appropriate attribute. The property manipulation method provided by XML comes from IXMLDOMElement, which can be set by the setAttribute method of IXMLDOMElement. Now analyze the properties of the template child elements:
a. Static lattice attribute. The content in the static grid has been determined at the time of table design. It needs to contain the "font" sub-element, which is used to set the attributes of the text. The font sub-element attributes include the font name, size, and so on.
b. Dynamic lattice attributes. The content in the dynamic grid is filled in by the user. You need to set the layout of the table. It contains fixed grid elements. In order to achieve association with the database, you also need to set the field name attribute and the corresponding database table name. Through this correspondence, not only the process data can be directly accessed in the database during process editing, but also the foundation for the open management of process data.
c. Loop lattice attribute. The properties of the loop are similar to the dynamic grid. Because it contains multiple rows of records, you need to set the row and column properties.
d. Object grid properties. A cell is a cell that fills in a process diagram or other complex data, and you need to set the source of the graph or other complex data.
e. Public properties of each object. Since each sub-element is a series of cells, it contains public attributes such as table coordinate values ​​and line shapes. You also need to set the card area properties for each cell. After defining the template sub-element properties, you need to save the results to add the graphic elements to the card template. In this case, you need to use the XML save method: m_pXMLDoc.save(sXMLDocName). After the save is successful, the graphical interface is updated to display the latest card template format.
3.4 Interactive adjustment of the template format
After each object of the template is generated, sometimes its format cannot meet the requirements, and a series of adjustments are needed to finally form a well-formed process template.
a. Adjustment of cell position. After selecting the cell to be adjusted, it can be adjusted by the position adjustment function of the system. There are two ways to implement cell position adjustment: primary adjustment and precise adjustment. The primary adjustment is to make a rough adjustment by moving the selected cells. The movement provides a "rubber strip" processing method, dynamically dragging coordinate values, including horizontal and vertical movement values.
b. Adjustment of cell size. Since the cells drawn during card customization are usually drawn arbitrarily, the size of the cells is often not accurate enough. Any function that changes the size of the cell, such as contour, equal width, and changing cell height, changing the cell width, is provided in the system. When the user selects a cell, a dialog box will pop up, and the user can adjust the height or width of the cell by inputting a specific value.
c. Adjustment of the field name. Sometimes the user needs to change the cell's field name to change its association with the database. As long as a cell is selected, the corresponding property setting dialog box will pop up, and the user can modify the field name of the cell.
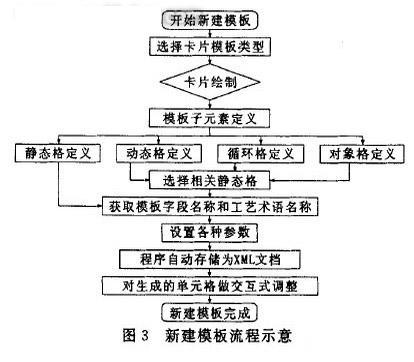
d. Adjustment of static grid attributes. The adjustment of the static grid content is similar to the adjustment of the field name. As long as the static grid needs to be adjusted, the property change dialog box will pop up, and the cell properties can be adjusted, including the adjustment of the text, font and alignment of the static grid. In summary, the user adjusts the size, position, and attributes of the generated template sub-elements in an interactive manner. After adjustment, the template customization work is completed. The template customization process is shown in Figure 3.
4 Conclusion
By decomposing the constituent elements of the craft card, the process template is abstracted into an entity consisting of a static grid, a dynamic grid, a object grid and a loop grid, and the process template is drawn and defined by interactive means, and the constructed process template is constructed. Saved as an XML document, the loading of the template sub-element is completed, thus implementing the customization process of the process template. Practice has proved that this interactive template customization technology is of great significance for realizing the versatility and commercialization of the CAPP system.
Previous page
Energy Conservation Transformation For 300Mw Coupling
Engery Conservation Transformation For 300Mw Coupling
Vertical Turbine Pump,Boiler Feed Pumps,Feed Pump,Viscous Coupling Modification
Shenyang pump products sales co., LTD , https://www.syipsc.com