China's renewable energy profile
2022-12-11 08:07:56
(I) Resource potential According to the preliminary resource evaluation, renewable energy resources with large potential and good prospects for development in China mainly include water, biomass, wind and solar energy.
1. Hydro-energy and hydro-energy resources are important renewable energy resources in China. According to the results of the national review of hydraulic resources in 2003, the installed capacity of hydropower resources in China is 540 million kilowatts, and the annual power generation is 2.47 trillion kilowatt-hours; the economically exploitable installed capacity is 400 million kilowatts, and the annual power generation is 1.75 trillion kwh. . Water energy resources are mainly distributed in the western region, and about 70% are in the southwest region. The Yangtze River, Jinsha River, Yalong River, Dadu River, Wujiang River, Hongshui River, Lancang River, Yellow River and Nujiang River have abundant hydropower resources in the main stream, and the total installed capacity accounts for about 60% of the national economically exploitable volume, with concentrated development. And good conditions for the delivery of the scale.
2. Biomass Energy China's biomass energy resources mainly include crop stalks, tree branches, livestock and poultry excrement, energy crops (plants), industrial organic waste water, urban domestic sewage, and garbage. The annual output of crop straws in the country is about 600 million tons. Except for some papermaking raw materials and animal husbandry feeds, about 300 million tons can be used as fuel, which amounts to 150 million tons of standard coal. The annual amount of forest branches and forestry wastes is about 900 million tons, and about 300 million tons can be used as energy sources, equivalent to 200 million tons of standard coal. The energy crops (plants) such as sweet sorghum, jatropha, berberine, and tung tree can be planted in an area of ​​more than 20 million hectares, which can meet the demand for raw materials for biological liquid fuels with an annual output of about 50 million tons. Livestock and aquaculture and industrial organic wastewater can theoretically produce about 80 billion cubic meters of biogas annually, and annual domestic urban garbage production is about 120 million tons. At present, the potential of China's biomass resources to be converted into energy is about 500 million tons of standard coal. With the expansion of afforestation area and economic and social development, the potential for conversion of biomass resources to energy can reach 1 billion tons of standard coal.
3. Wind energy According to the latest evaluation of wind energy resources, the country's land can use 300 million kilowatts of wind energy resources, plus wind energy resources available in coastal waters, totaling about 1 billion kilowatts. It is mainly distributed in two major wind zones: the first is the “Three North Regions†(northeast, northern North China, and northwest regions), and the second is the eastern coastal land, islands, and near-shore waters. In addition, there are some local wind energy-rich areas in the inland areas.
(4) Solar two-thirds of the country's total annual sunshine hours is more than 2,200 hours, and the annual total solar radiation is more than 5,000 megajoules per square meter, which is a region with better solar energy utilization conditions. The solar radiation energy in Tibet, Qinghai, Xinjiang, Gansu, Inner Mongolia, Shanxi, Shaanxi, Hebei, Shandong, Liaoning, Jilin, Yunnan, Guangdong, Fujian and Hainan is relatively large, especially in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau.
5. Geothermal energy According to preliminary exploration, China's geothermal resources are mainly low-temperature, which is suitable for industrial heating, building heating, health care and health care, and planting and breeding. Resources are found throughout the country. The high-temperature geothermal resources suitable for power generation are few and are mainly distributed in southern Tibet, western Sichuan, and western Yunnan, and the installed potential is about 6 million kilowatts. According to preliminary estimates, the national renewable geothermal resources amount to approximately 3.3 billion tons of standard coal.
(II) Development Status After years of development, China has made great achievements in renewable energy, and hydropower has become an important part of the power industry. Combined with rural energy and ecological construction, household biogas has been widely used. In recent years, significant progress has also been made in wind power, photovoltaic power generation, solar thermal utilization, and efficient utilization of biomass energy, and has made significant contributions to the adjustment of energy structure, protection of the environment, and promotion of economic and social development.
In 2005, the total amount of renewable energy development and utilization (excluding conventional use of biomass energy) was approximately 166 million tons of standard coal, which was approximately 7.5% of the country's total primary energy consumption in 2005.
1. Hydropower By the end of 2005, the total installed hydropower capacity of the country reached 117 million kilowatts (including about 7 million kilowatts of pumped-storage power stations), which accounted for 23% of the country's total installed power generation capacity, and the annual hydropower generation capacity was 395.2 billion kwh, accounting for the entire country. 16% of total electricity generation. Among them, 38 million kilowatts of small hydropower and an annual power generation of about 130 billion kwh are responsible for the power supply of nearly one-half of the country’s land area, one-third of the counties, and one-quarter of the population. A total of 653 primary electrification counties for rural hydropower have been established in the country, and 400 electrified counties focusing on small hydropower are currently being constructed. China's hydropower survey, design, construction, installation and equipment manufacturing have reached the international level and a complete industrial system has been formed.
2. Biomass Energy (1) Biogas. By the end of 2005, the number of household biogas digesters in the country has reached 18 million, and the annual production of biogas is about 7 billion cubic meters. About 1,500 biogas projects and industrial organic waste water biogas projects have been completed, with an annual output of about 1 billion cubic meters of biogas. . Biogas technology has evolved from simple energy utilization to waste treatment and multi-level comprehensive utilization of biomass, and has been extensively integrated with aquaculture and planting industries, and has become an important approach to the development of green ecological agriculture and the consolidation of ecological construction achievements. The components of the biogas project have achieved standardized production and the biogas technical service system has been relatively complete.
(2) Biomass power generation. By the end of 2005, the installed capacity of biomass power generation in the country was about 2 million kilowatts, of which bagasse power generation was about 1.7 million kilowatts, garbage power generation was about 200,000 kilowatts, and the rest were gasification power generation from agricultural and forestry waste, such as rice husks, and biogas power generation. On the basis of the introduction of foreign waste incineration power generation technologies and equipment, after digestion and absorption, it is now basically capable of manufacturing waste incineration power generation equipment. The introduction of foreign equipment and technology has built some landfill gas demonstration projects. In general, however, there is still a certain gap between China and the international advanced level in terms of raw material collection, purification treatment, and manufacturing of combustion equipment for biomass power generation.
(3) Biological liquid fuels. China has begun to use fuel ethanol in transportation fuels. The annual production capacity of fuel ethanol with grain as raw material is 1.02 million tons; the technology for producing fuel ethanol from non-food materials has initially met the conditions for commercial development. The biodiesel production capacity of catering industry waste oil, oil mill oil slag, and oil crops has reached an annual production capacity of 50,000 tons.
3. Wind Power By the end of 2005, more than 60 grid-connected wind farms have been built across the country, with a total installed capacity of 1.26 million kilowatts. In addition, there are approximately 250,000 small independent wind turbine generators (a total capacity of approximately 50,000 kilowatts) in remote areas. China's single-capacity capacity of 750 kilowatts or less of wind power equipment has been mass-produced and is developing wind turbines with a MW level (1000 kilowatts) or more. Compared with the international advanced level, the domestic wind turbine unit has a small stand-alone capacity, and key technologies depend on imports. The quality of parts and components needs to be improved.
4, solar energy (1) solar power generation. By the end of 2005, the total capacity of photovoltaic power generation in the country was about 70,000 kilowatts, which was mainly to supply electricity to residents in remote areas. The “Power Transmission to Township†project implemented from 2002 to 2003 installed about 19,000 kilowatts of photovoltaic cells, which played a significant role in the application of photovoltaic power generation and photovoltaic cell manufacturing. In addition to using photovoltaic power to supply electricity to remote areas and special areas (communications, navigation, and transportation), the demonstration project of rooftop grid-connected photovoltaic power generation has begun. There are more than a dozen photovoltaic cells and assembly plants with an annual production capacity of more than 100,000 kilowatts. In general, however, the overall level of China's photovoltaic power generation industry is still far behind that of developed countries. In particular, the silicon materials required for the production of photovoltaic cells rely mainly on imports, which poses a major constraint on the industrial development of photovoltaic power generation in China.
(2) Solar water heaters. By the end of 2005, the total area of ​​solar water heaters in use in China reached 80 million square meters, and the annual production capacity was 15 million square meters. There are more than 1,000 manufacturers of solar water heaters in the country. The total annual production value is nearly 12 billion yuan, and a relatively complete industrial system has been formed. The number of employees in the industry is more than 200,000. Overall, there is still a gap between China's solar water heater application technology and developed countries. At present, the solar water heaters in developed countries have achieved a better combination with the building, and they have developed toward the integration of solar energy buildings, and China has only started to develop in this respect.
5. The geothermal energy geothermal power generation technology is divided into geothermal water steam power generation and low-boiling point organic power generation. Geothermal resources suitable for power generation in China are concentrated in Tibet and Yunnan. Due to the abundant local water resources, geothermal power generation is not competitive, and it is difficult to develop in large scale in the near future. In recent years, the heat utilization of geothermal energy has developed rapidly, mainly due to hot water supply and heating, water source heat pumps, and ground source heat pump heating and cooling. With the continuous strengthening of the protection of groundwater resources, the direct use of geothermal water will be subject to more restrictions. Ground source heat pump will be the main direction of development in the future.
(III) Problems Although China has made great achievements in the development and utilization of renewable energy, and the laws and regulations and policy systems have been continuously improved, the development of renewable energy cannot meet the needs of sustainable development. The main problems are:
(1) Policies and incentives are insufficient. In the current state of technology and policy environment, in addition to the ability of hydropower and solar water heaters to participate in market competition, most renewable energy development and utilization costs are high, coupled with the characteristics of scattered resources, small scale, and discontinuous production, in the current market. Lack of competitiveness under the rules requires policy support and incentives. At present, the state's policy system for supporting the development of renewable energy such as wind power, biomass, and solar energy is not yet complete, economic incentives are weak, there is a lack of coordination between related policies, and the stability of policies is poor, and there is no long-term support for the sustainable development of renewable energy. Effect mechanism.
(2) The market protection mechanism is still not perfect. For a long time, the development of renewable energy in our country lacks a clear development goal and has not formed a continuous and stable market demand. Although the country has gradually increased its support for the development of renewable energy, it has failed to establish a mandatory market protection policy and cannot form a stable market demand. The lack of sustained market development in the development of renewable energy has resulted in a new renewable energy source in China. Slow technology development.
(3) Technology development capabilities and industrial systems are weak. Except for hydroelectric power generation, solar thermal utilization and biogas, other renewable energy technologies have a low level of technology, lack of technological research and development capabilities, weak equipment manufacturing capabilities, and the production of technologies and equipment relies more on imports. The gap between technological level and production capacity and advanced foreign standards Larger. At the same time, the evaluation of renewable energy resources, technical standards, product testing and certification systems are incomplete, and personnel training cannot meet the requirements of rapid market development. There is no technical service system that supports the development of the renewable energy industry.
1. Hydro-energy and hydro-energy resources are important renewable energy resources in China. According to the results of the national review of hydraulic resources in 2003, the installed capacity of hydropower resources in China is 540 million kilowatts, and the annual power generation is 2.47 trillion kilowatt-hours; the economically exploitable installed capacity is 400 million kilowatts, and the annual power generation is 1.75 trillion kwh. . Water energy resources are mainly distributed in the western region, and about 70% are in the southwest region. The Yangtze River, Jinsha River, Yalong River, Dadu River, Wujiang River, Hongshui River, Lancang River, Yellow River and Nujiang River have abundant hydropower resources in the main stream, and the total installed capacity accounts for about 60% of the national economically exploitable volume, with concentrated development. And good conditions for the delivery of the scale.
2. Biomass Energy China's biomass energy resources mainly include crop stalks, tree branches, livestock and poultry excrement, energy crops (plants), industrial organic waste water, urban domestic sewage, and garbage. The annual output of crop straws in the country is about 600 million tons. Except for some papermaking raw materials and animal husbandry feeds, about 300 million tons can be used as fuel, which amounts to 150 million tons of standard coal. The annual amount of forest branches and forestry wastes is about 900 million tons, and about 300 million tons can be used as energy sources, equivalent to 200 million tons of standard coal. The energy crops (plants) such as sweet sorghum, jatropha, berberine, and tung tree can be planted in an area of ​​more than 20 million hectares, which can meet the demand for raw materials for biological liquid fuels with an annual output of about 50 million tons. Livestock and aquaculture and industrial organic wastewater can theoretically produce about 80 billion cubic meters of biogas annually, and annual domestic urban garbage production is about 120 million tons. At present, the potential of China's biomass resources to be converted into energy is about 500 million tons of standard coal. With the expansion of afforestation area and economic and social development, the potential for conversion of biomass resources to energy can reach 1 billion tons of standard coal.
3. Wind energy According to the latest evaluation of wind energy resources, the country's land can use 300 million kilowatts of wind energy resources, plus wind energy resources available in coastal waters, totaling about 1 billion kilowatts. It is mainly distributed in two major wind zones: the first is the “Three North Regions†(northeast, northern North China, and northwest regions), and the second is the eastern coastal land, islands, and near-shore waters. In addition, there are some local wind energy-rich areas in the inland areas.
(4) Solar two-thirds of the country's total annual sunshine hours is more than 2,200 hours, and the annual total solar radiation is more than 5,000 megajoules per square meter, which is a region with better solar energy utilization conditions. The solar radiation energy in Tibet, Qinghai, Xinjiang, Gansu, Inner Mongolia, Shanxi, Shaanxi, Hebei, Shandong, Liaoning, Jilin, Yunnan, Guangdong, Fujian and Hainan is relatively large, especially in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau.
5. Geothermal energy According to preliminary exploration, China's geothermal resources are mainly low-temperature, which is suitable for industrial heating, building heating, health care and health care, and planting and breeding. Resources are found throughout the country. The high-temperature geothermal resources suitable for power generation are few and are mainly distributed in southern Tibet, western Sichuan, and western Yunnan, and the installed potential is about 6 million kilowatts. According to preliminary estimates, the national renewable geothermal resources amount to approximately 3.3 billion tons of standard coal.
(II) Development Status After years of development, China has made great achievements in renewable energy, and hydropower has become an important part of the power industry. Combined with rural energy and ecological construction, household biogas has been widely used. In recent years, significant progress has also been made in wind power, photovoltaic power generation, solar thermal utilization, and efficient utilization of biomass energy, and has made significant contributions to the adjustment of energy structure, protection of the environment, and promotion of economic and social development.
In 2005, the total amount of renewable energy development and utilization (excluding conventional use of biomass energy) was approximately 166 million tons of standard coal, which was approximately 7.5% of the country's total primary energy consumption in 2005.
1. Hydropower By the end of 2005, the total installed hydropower capacity of the country reached 117 million kilowatts (including about 7 million kilowatts of pumped-storage power stations), which accounted for 23% of the country's total installed power generation capacity, and the annual hydropower generation capacity was 395.2 billion kwh, accounting for the entire country. 16% of total electricity generation. Among them, 38 million kilowatts of small hydropower and an annual power generation of about 130 billion kwh are responsible for the power supply of nearly one-half of the country’s land area, one-third of the counties, and one-quarter of the population. A total of 653 primary electrification counties for rural hydropower have been established in the country, and 400 electrified counties focusing on small hydropower are currently being constructed. China's hydropower survey, design, construction, installation and equipment manufacturing have reached the international level and a complete industrial system has been formed.
2. Biomass Energy (1) Biogas. By the end of 2005, the number of household biogas digesters in the country has reached 18 million, and the annual production of biogas is about 7 billion cubic meters. About 1,500 biogas projects and industrial organic waste water biogas projects have been completed, with an annual output of about 1 billion cubic meters of biogas. . Biogas technology has evolved from simple energy utilization to waste treatment and multi-level comprehensive utilization of biomass, and has been extensively integrated with aquaculture and planting industries, and has become an important approach to the development of green ecological agriculture and the consolidation of ecological construction achievements. The components of the biogas project have achieved standardized production and the biogas technical service system has been relatively complete.
(2) Biomass power generation. By the end of 2005, the installed capacity of biomass power generation in the country was about 2 million kilowatts, of which bagasse power generation was about 1.7 million kilowatts, garbage power generation was about 200,000 kilowatts, and the rest were gasification power generation from agricultural and forestry waste, such as rice husks, and biogas power generation. On the basis of the introduction of foreign waste incineration power generation technologies and equipment, after digestion and absorption, it is now basically capable of manufacturing waste incineration power generation equipment. The introduction of foreign equipment and technology has built some landfill gas demonstration projects. In general, however, there is still a certain gap between China and the international advanced level in terms of raw material collection, purification treatment, and manufacturing of combustion equipment for biomass power generation.
(3) Biological liquid fuels. China has begun to use fuel ethanol in transportation fuels. The annual production capacity of fuel ethanol with grain as raw material is 1.02 million tons; the technology for producing fuel ethanol from non-food materials has initially met the conditions for commercial development. The biodiesel production capacity of catering industry waste oil, oil mill oil slag, and oil crops has reached an annual production capacity of 50,000 tons.
3. Wind Power By the end of 2005, more than 60 grid-connected wind farms have been built across the country, with a total installed capacity of 1.26 million kilowatts. In addition, there are approximately 250,000 small independent wind turbine generators (a total capacity of approximately 50,000 kilowatts) in remote areas. China's single-capacity capacity of 750 kilowatts or less of wind power equipment has been mass-produced and is developing wind turbines with a MW level (1000 kilowatts) or more. Compared with the international advanced level, the domestic wind turbine unit has a small stand-alone capacity, and key technologies depend on imports. The quality of parts and components needs to be improved.
4, solar energy (1) solar power generation. By the end of 2005, the total capacity of photovoltaic power generation in the country was about 70,000 kilowatts, which was mainly to supply electricity to residents in remote areas. The “Power Transmission to Township†project implemented from 2002 to 2003 installed about 19,000 kilowatts of photovoltaic cells, which played a significant role in the application of photovoltaic power generation and photovoltaic cell manufacturing. In addition to using photovoltaic power to supply electricity to remote areas and special areas (communications, navigation, and transportation), the demonstration project of rooftop grid-connected photovoltaic power generation has begun. There are more than a dozen photovoltaic cells and assembly plants with an annual production capacity of more than 100,000 kilowatts. In general, however, the overall level of China's photovoltaic power generation industry is still far behind that of developed countries. In particular, the silicon materials required for the production of photovoltaic cells rely mainly on imports, which poses a major constraint on the industrial development of photovoltaic power generation in China.
(2) Solar water heaters. By the end of 2005, the total area of ​​solar water heaters in use in China reached 80 million square meters, and the annual production capacity was 15 million square meters. There are more than 1,000 manufacturers of solar water heaters in the country. The total annual production value is nearly 12 billion yuan, and a relatively complete industrial system has been formed. The number of employees in the industry is more than 200,000. Overall, there is still a gap between China's solar water heater application technology and developed countries. At present, the solar water heaters in developed countries have achieved a better combination with the building, and they have developed toward the integration of solar energy buildings, and China has only started to develop in this respect.
5. The geothermal energy geothermal power generation technology is divided into geothermal water steam power generation and low-boiling point organic power generation. Geothermal resources suitable for power generation in China are concentrated in Tibet and Yunnan. Due to the abundant local water resources, geothermal power generation is not competitive, and it is difficult to develop in large scale in the near future. In recent years, the heat utilization of geothermal energy has developed rapidly, mainly due to hot water supply and heating, water source heat pumps, and ground source heat pump heating and cooling. With the continuous strengthening of the protection of groundwater resources, the direct use of geothermal water will be subject to more restrictions. Ground source heat pump will be the main direction of development in the future.
(III) Problems Although China has made great achievements in the development and utilization of renewable energy, and the laws and regulations and policy systems have been continuously improved, the development of renewable energy cannot meet the needs of sustainable development. The main problems are:
(1) Policies and incentives are insufficient. In the current state of technology and policy environment, in addition to the ability of hydropower and solar water heaters to participate in market competition, most renewable energy development and utilization costs are high, coupled with the characteristics of scattered resources, small scale, and discontinuous production, in the current market. Lack of competitiveness under the rules requires policy support and incentives. At present, the state's policy system for supporting the development of renewable energy such as wind power, biomass, and solar energy is not yet complete, economic incentives are weak, there is a lack of coordination between related policies, and the stability of policies is poor, and there is no long-term support for the sustainable development of renewable energy. Effect mechanism.
(2) The market protection mechanism is still not perfect. For a long time, the development of renewable energy in our country lacks a clear development goal and has not formed a continuous and stable market demand. Although the country has gradually increased its support for the development of renewable energy, it has failed to establish a mandatory market protection policy and cannot form a stable market demand. The lack of sustained market development in the development of renewable energy has resulted in a new renewable energy source in China. Slow technology development.
(3) Technology development capabilities and industrial systems are weak. Except for hydroelectric power generation, solar thermal utilization and biogas, other renewable energy technologies have a low level of technology, lack of technological research and development capabilities, weak equipment manufacturing capabilities, and the production of technologies and equipment relies more on imports. The gap between technological level and production capacity and advanced foreign standards Larger. At the same time, the evaluation of renewable energy resources, technical standards, product testing and certification systems are incomplete, and personnel training cannot meet the requirements of rapid market development. There is no technical service system that supports the development of the renewable energy industry.
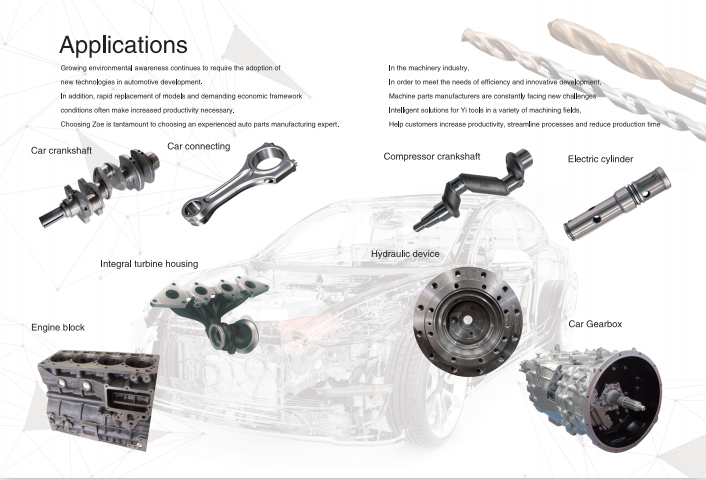
Deep hole drilling can also be used in cross-hole occasions or where the workpiece has an inclined surface, which can improve productivity for customers and reduce the processing cost of unit holes. Extend the service life of the tool.
The company has a number of imported CNC
grinding machines, including 6 sets Walter CNC grinding machines, and a
number of high-precision imported tool testing equipment. The tool
quality is trustworthy.
Deep Hole Twist Drill,Extra Long Drill Bits For Concrete,Long Twist Drills,Long Countersink Drill Bit
ROYI CNC TOOL TAIXING CITY CO.,LTD , https://www.royitools.com