Analysis of the application of threaded fasteners in automobile assembly
Threaded fastener connections are one of the most common ways of connecting cars, including welding, riveting and adhesive bonding. The purpose of the threaded fastener connection is to make the connected parts closely fit and bear a certain external force, and has the advantages of high precision, convenient assembly and convenient assembly and disassembly of parts.
There are four kinds of external forces applied to the threaded joints, tensile stress, shearing force, tensile stress + bending stress, tensile stress + bending stress + shear stress. To ensure that the threaded fastener connection can overcome various static external forces or dynamic external forces on the connected components, the threaded fasteners will generate an axial clamping force on the connected components. The applied torque is provided. The bolt overcomes the frictional force and elastically deforms according to the rigidity ratio relationship between the bolt and the connected component, thereby forming a clamping force between the bonding surfaces at both ends of the bolt. The correct tightening process should control this clamping force, so the essence of the assembly tightening is to control the axial clamping force of the bolt to an appropriate range.
During the assembly of the threaded fastener connection, the dispersion of the clamping force is affected by the selected assembly method and other external conditions. When assembling, the clamping force must be large enough to ensure that the connected parts can be reliably fitted during operation without relative movement; on the other hand, the applied clamping force must ensure the bolts and connected parts. No damage or plastic deformation occurs during assembly and service. Market research shows that most of the problems that arise in bolted joints, such as loose bolts, broken joints, crushing and damage of connected parts, are caused by inaccurate or incorrect clamping forces. Studies have shown that the greater the axial clamping force of the bolt, the better the anti-loose and anti-fatigue properties of the bolt, and usually the best effect is obtained when the bolt is tightened to yield.
At the car assembly site, the clamping force of each bolting pair cannot be measured correctly considering the actual production cycle and operation. Therefore, the torque can be used as the intermediate value to evaluate the assembly quality of the bolting pair. For torque control, the tightening accuracy of the tightening tool and the tightening process are two key factors. Under normal circumstances, the torque control accuracy of pneumatic tools is 10% to 40%; the accuracy of manual torque wrenches is about 10%; the control torque of electric tightening machines can reach 3% to 5%. The tightening tool and the precision of the control directly determine the level of assembly.
The domestic automotive industry standard QC/T518-2013 automotive thread fastener fastening torque is divided into three levels of fastener tightening accuracy, I, II, III, different levels of torque tolerance corresponding torque The tolerance and torque ratio are shown in Table 1.Table 1 Torque ratio corresponding to different levels of tightening accuracy
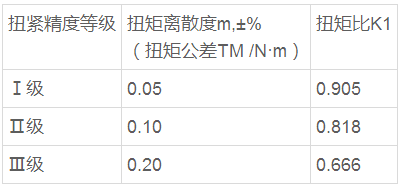
Note: K1=tightening torque minimum/tightening torque maximumFor example, the M20X1.5X100 hex bolt with a 10.9 friction coefficient of 0.12 is used. When the III-stage assembly is used, the target tightening torque is small, and the torque fluctuation range is large, the clamping force on the thread is minimized, and the target fastening is improved after the assembly level. The torque is increased, and the torque fluctuation range becomes smaller, and the clamping force is increased. The target torque of the Class I assembly is increased by 0.087% compared to the Class III assembly, and the clamping force acting on the thread is increased by 32.5%. According to the foreign thread fastener assembly standard, when the thread connection level is III, if the M16 bolt is used, the requirements can be met; when the level I assembly is selected, the bolt size can be reduced to M12. It is necessary to grade the assembly of automotive threaded fasteners. When the fastener supplier receives the order, first consider the requirements of the technical agreement. Compared with the III-level assembly, the I-level assembly is used, the target tightening torque of the bolt is increased, the torque fluctuation range is reduced, and the clamp on the bolt is reduced. The tightening force is improved; when the connection structure requires the clamping force of the bolt to be constant, the I-level assembly is adopted, the bolt size can be reduced, the weight reduction and weight reduction are realized, and the structure is compact.
Sf6 Gas Density Meter,Natural Gas Density Meter,Lpg Density Meter,Oxygen Density Meter
wuxi kaifeng pressure gauge co., ltd , https://www.wxkfmanometer.com